Consistent with model predictions, a warmer Arctic is increasingly a wetter one.
With the third La Niña winter in a row well underway, our blogger takes a look at how La Niña influences the range of winter daily temperatures.
Recent research has suggested possible ozone recovery in the upper stratosphere and decreasing ozone in the lower stratosphere. A new study supports a declining ozone trend in the lower stratosphere but no ozone “recovery” in the upper stratosphere.
A new study examines how rising global temperatures may affect weather patterns in the region stretching from the east coasts of China and Taiwan, and Japan.
A new story map recounts how NOAA scientists raced against nature to save their most valuable scientific instruments in the Bering Sea in 2021. This interactive map highlights the recovery efforts, unique data collected, and implications for management.
November 30 marked the official end to the 2022 Atlantic hurricane season. This year, NOAA’s AOML coordinated the longest series of missions into a single tropical system, deployed new uncrewed aircraft technology, and included a novel capability in hurricane modeling.
NOAA has released a new strategy and invited the public to listening sessions to guide the agency’s potential role in carbon dioxide removal from Earth’s atmosphere. Virtual sessions are scheduled for Mon Dec 12 @ 3 p.m. ET, and Weds Dec 14 at 10 a.m. and 5 p.m. ET. Registration required.
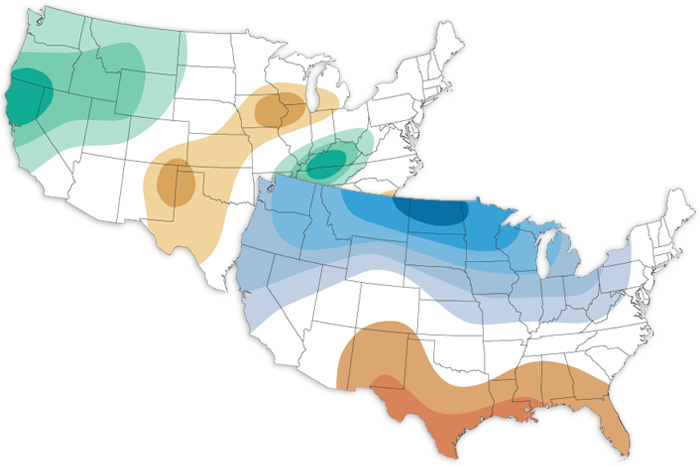
The December 2022 climate outlook favors a colder-than-average month across the northern US, and a warmer-than-average month across the southern US. Meanwhile, odds are tilted towards a wetter-than-average December for the West and Ohio and Tennessee Valleys.
Join us for the NOAA’s Geostationary Extended Observations (GeoXO) Satellite Atmospheric Composition Capabilities Town Hall at the AGU 2022 Fall Meeting on Thursday, December 15, 2022. NOAA’s GeoXO mission is a ground-breaking effort to address future environmental challenges in support of U.S. weather, ocean, and climate operations.
A new study suggests that ships may be spreading stony coral tissue loss disease across Florida and the Caribbean. Experiments used ultraviolet treatment of ship ballast water to see if it could transport pathogens, and whether ultraviolet treatment of this water could prevent the spread of this disease.