What evidence exists that Earth is warming and that humans are the main cause?
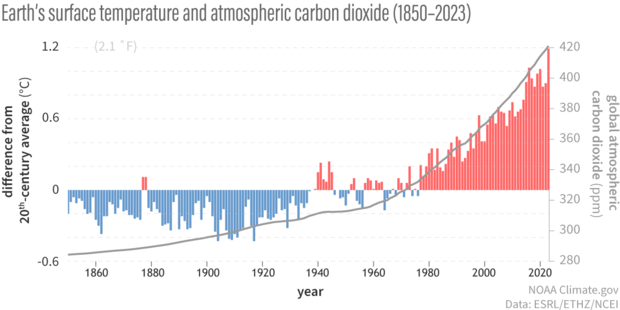
We know the world is warming because people have been recording daily high and low temperatures at thousands of weather stations worldwide, over land and ocean, for many decades and, in some locations, for more than a century. When different teams of climate scientists in different agencies (e.g., NOAA and NASA) and in other countries (e.g., the U.K.’s Hadley Centre) average these data together, they all find essentially the same result: Earth’s average surface temperature has risen by about 1.8°F (1.0°C) since 1880.
(bar chart) Yearly temperature compared to the twentieth-century average from 1850–2023. Red bars mean warmer-than-average years; blue bars mean colder-than-average years. (line graph) Atmospheric carbon dioxide amounts: 1850-1958 from IAC, 1959-2023 from NOAA Global Monitoring Lab. NOAA Climate.gov graph, adapted from original by Dr. Howard Diamond (NOAA ARL).
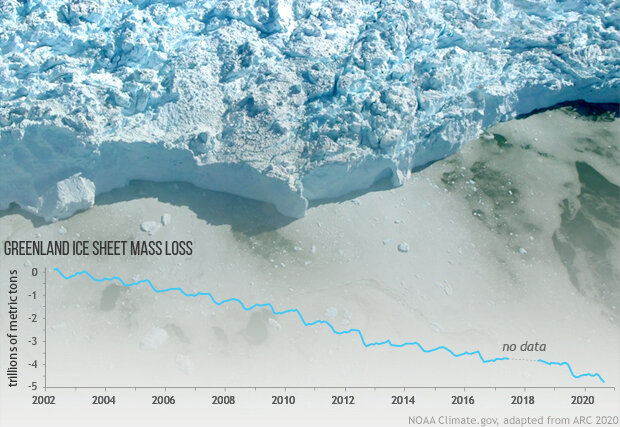
In addition to our surface station data, we have many different lines of evidence that Earth is warming (learn more). Birds are migrating earlier, and their migration patterns are changing. Lobsters and other marine species are moving north. Plants are blooming earlier in the spring. Mountain glaciers are melting worldwide, and snow cover is declining in the Northern Hemisphere (Learn more here and here). Greenland’s ice sheet—which holds about 8 percent of Earth’s fresh water—is melting at an accelerating rate (learn more). Mean global sea level is rising (learn more). Arctic sea ice is declining rapidly in both thickness and extent (learn more).
The Greenland Ice Sheet lost mass again in 2020, but not as much as it did 2019. Adapted from the 2020 Arctic Report Card, this graph tracks Greenland mass loss measured by NASA's GRACE satellite missions since 2002. The background photo shows a glacier calving front in western Greenland, captured from an airplane during a NASA Operation IceBridge field campaign. Full story.
We know this warming is largely caused by human activities because the key role that carbon dioxide plays in maintaining Earth’s natural greenhouse effect has been understood since the mid-1800s. Unless it is offset by some equally large cooling influence, more atmospheric carbon dioxide will lead to warmer surface temperatures. Since 1800, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased from about 280 parts per million to 410 ppm in 2019. We know from both its rapid increase and its isotopic “fingerprint” that the source of this new carbon dioxide is fossil fuels, and not natural sources like forest fires, volcanoes, or outgassing from the ocean.
Philip James de Loutherbourg's 1801 painting, Coalbrookdale by Night, came to symbolize the start of the Industrial Revolution, when humans began to harness the power of fossil fuels—and to contribute significantly to Earth's atmospheric greenhouse gas composition. Image from Wikipedia.
Finally, no other known climate influences have changed enough to account for the observed warming trend. Taken together, these and other lines of evidence point squarely to human activities as the cause of recent global warming.
References
USGCRP (2017). Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume 1 [Wuebbles, D.J., D.W. Fahey, K.A. Hibbard, D.J. Dokken, B.C. Stewart, and T.K. Maycock (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, 470 pp, doi: 10.7930/J0J964J6.
National Fish, Wildlife, and Plants Climate Adaptation Partnership (2012): National Fish, Wildlife, and Plants Climate Adaptation Strategy. Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies, Council on Environmental Quality, Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Washington, D.C. DOI: 10.3996/082012-FWSReport-1
IPCC (2019). Summary for Policymakers. In: IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.)]. In press.
NASA JPL: "Consensus: 97% of climate scientists agree." Global Climate Change. A website at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (climate.nasa.gov/scientific-consensus). (Accessed July 2013.)