Overview of conditions
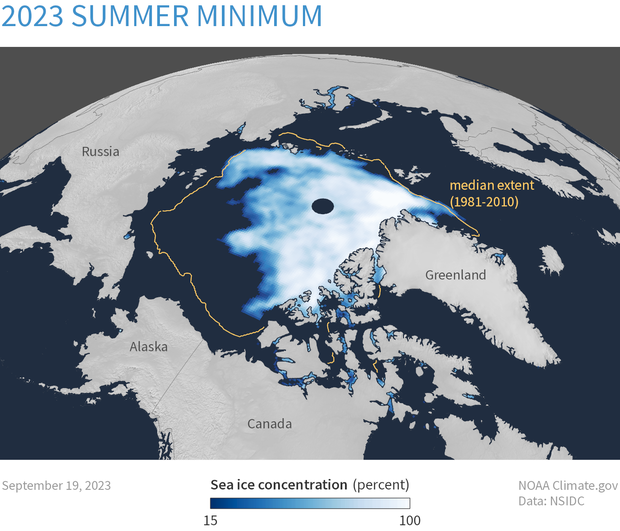
On September 19, sea ice reached its annual minimum extent of 4.23 million square kilometers (1.63 million square miles). As the sun continues to lower on the horizon, air temperatures will drop further, expanding ice extent through autumn and winter. However, with significant patches of low ice concentration a late season storm may compress the sea ice and push the ice extent lower.
Arctic sea ice extent for September 19 2023, was 4.23 million square kilometers (1.63 million square miles). It was the sixth smallest summer minimum on record. The orange line shows the 1981 to 2010 average extent for that day. NOAA Climate.gov image, based on data from the National Snow and Ice Data Center.
The minimum extent was reached five days later than the 1981 to 2010 median minimum date of September 14. The interquartile range of minimum dates is September 11 to September 19.
Conditions in context
This year’s minimum set on September 19 was 840,000 square kilometers (324,000 square miles) above the satellite-era record minimum extent of 3.39 million square kilometers (1.31 million square miles), which occurred on September 17, 2012 (Figure 2). It is also 1.99 million square kilometers (770,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 average minimum extent, which is equivalent to nearly three times the size of Texas.
The overall, downward trend in the minimum extent from 1979 to 2023 is 12.5 percent per decade relative to the 1981 to 2010 average. The loss of sea ice is about 77,800 square kilometers (30,000 square miles) per year, equivalent to losing the state of Nebraska or the Czech Republic annually.
For more information, read the full story from the National Snow and Ice Data Center.