
In the midst of a drought in 2008, biologists discovered dead Coho and steelhead trout in a tributary of the Russian River. When the dust settled, the focus turned to how winegrowers and other water users could reduce their impact. The event provided the parties involved—winegrowers, conservationists, and the water agency—an opportunity to find common ground in the realm of science.
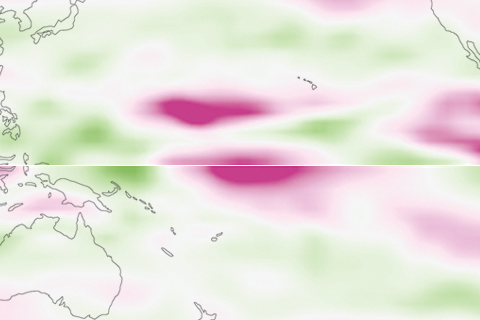
Add a new item to the list of things that have migrated in response to climate change: the latitude where hurricanes reach their maximum intensity. The shift was accompanied by increasing vertical wind shear near the equator.

On August 25, 2011, Dr. Elwynn Taylor, Iowa State University's Extension Climatologist, tweeted to Iowa corn farmers: “Weather based statistics indicate a US corn yield of 149BPA, the prime factor this year is the Aridity Index.” Taylor uses NOAA climate information and seasonal outlooks to help thousands of the region's farmers manage risk. Nearly 5,000 followers look to his Twitter feed for guidance.

Since 2004, researchers in NOAA’s Global Monitoring Division have released the Annual Greenhouse Gas Index: a single value that compares the total warming effect of each year's concentrations of heat-trapping gases to 1990 levels.

In response to recent decades' warming, forests in the eastern United States have been "inhaling" more carbon dioxide through photosynthesis than they've “exhaled” through respiration.

In April 2011, Texas was in the midst of what may have been its worst fire season in history. As the season began, NOAA outlooks and observations helped fire managers think strategically about where their resources could be most effective.
CarbonTracker is a tool for modelling sources and sinks of carbon dioxide. Users can download the code, carbon dioxide data, and the tool's carbon flux estimates to conduct their own analyses or to help improve the system.
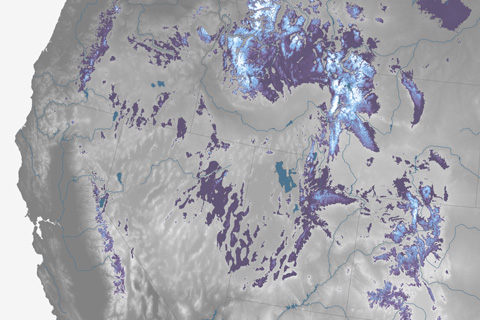
Variability in snowpack across the mountain ranges of the U.S. West at the start of the warm season can translate into big differences in fire risk and summer water stress.

Ocean water acidified by increasing carbon dioxide is corroding calcium carbonate minerals—an essential ingredient for shell- and skeleton-building that creatures like this tiny snail rely upon.

Like a prehistoric fly trapped in amber during dinosaurs' days, airborne relics of Earth's earlier climate can end up trapped in glacial ice for eons. How do climate scientists turn those tiny relics into a story about Earth's ancient climate?