National Climate Assessment: Great Plains’ Ogallala Aquifer drying out
Details
The Ogallala Aquifer underlies parts of Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming. From wheat and cows to corn and cotton, the regional economy depends almost exclusively on agriculture irrigated by Ogallala groundwater. But according to the Fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4), producers are extracting water faster than it is being replenished, which means that parts of the Ogallala Aquifer should be considered a nonrenewable resource.
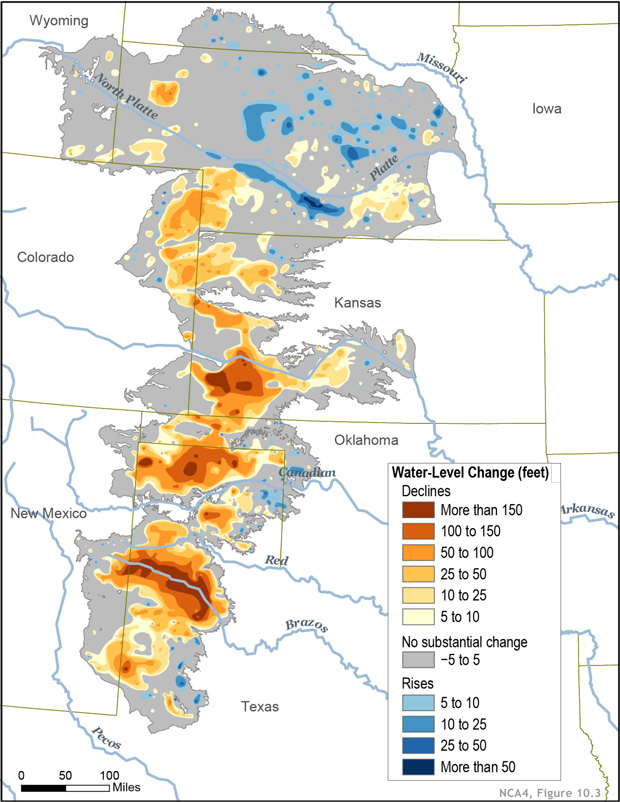
This map shows changes in Ogallala water levels from the period before the aquifer was tapped to 2015. Declining levels appear in red and orange, and rising levels appear in shades of blue. The darker the color, the greater the change. Gray indicates no significant change. Although water levels have actually risen in some areas, especially Nebraska, water levels are mostly in decline, namely from Kansas southward.
In the early twentieth century, farmers converted large stretches of the Great Plains from grassland to cropland. Drought and stress on the soils led to the 1930s Dust Bowl. Better soil conservation and irrigation techniques tamed the dust and boosted the regional economy. In 2007, the market value from the Ogallala region's agricultural products totaled roughly $35 billion. However, well outputs in the central and southern parts of the aquifer are declining due to excessive pumping, and prolonged droughts have parched the area, bringing back Dust Bowl-style storms, according to the NCA4. Global warming is likely to make droughts across the Ogallala region longer lasting and more intense over the next 50 years.
The Agriculture chapter of NCA4 describes the risks and opportunities for resilience across the Ogallala region:
Recent advances in precision irrigation technologies, improved understanding of the impacts of different dryland and irrigation management strategies on crop productivity, and the adoption of weather-based irrigation scheduling tools as well as drought-tolerant crop varieties have increased the ability to cope with projected heat stress and drought conditions under climate change. However, current extraction for irrigation far exceeds recharge in this aquifer, and climate change places additional pressure on this critical water resource.
References
Gowda, P., Steiner, J.L., Olson, C., Boggess, M., Farrigan, T., Grusak, M.A. (2018). Chapter 10: Agriculture and Rural Communities. Fourth National Climate Assessment.
McGuire, V.L. (2017). Water-level and recoverable water in storage changes, High Plains aquifer, predevelopment to 2015 and 2013–15. Scientific Investigations Report 2017-5040. U.S. Geological Survey. doi:10.3133/sir20175040.