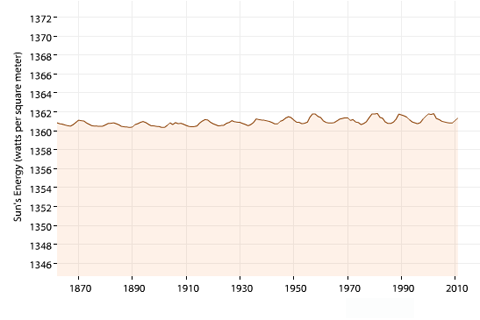
The Sun's average brightness varies over time, and the changes can affect global surface temperature. But long-term changes over the period of human-caused global warming are minimal.
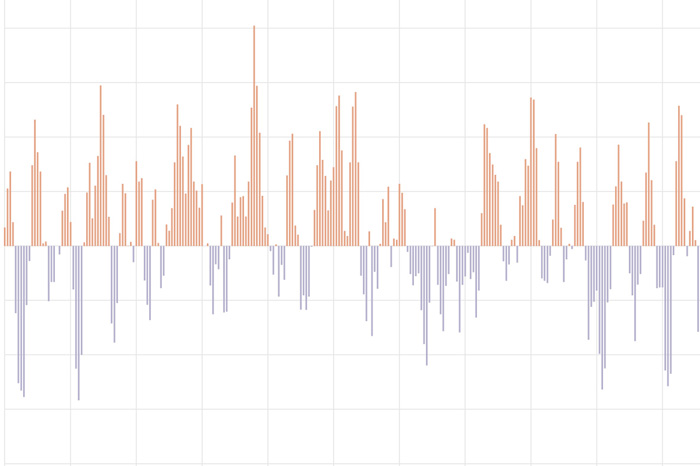
The Pacific-North American teleconnection pattern influences regional weather by affecting the strength and location of the East Asian jet stream, and subsequently, the weather it delivers to North America.
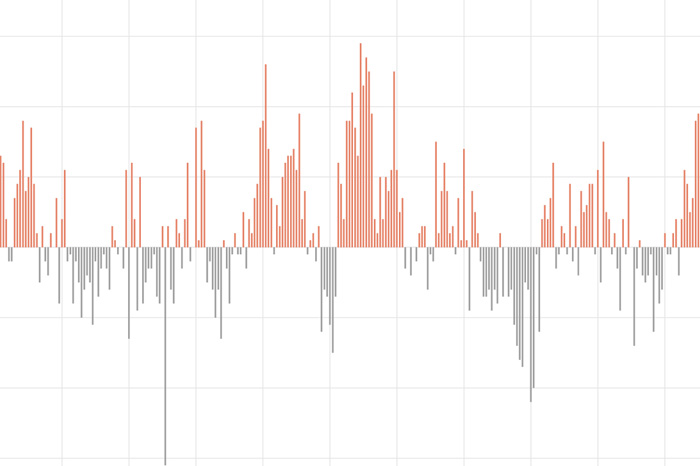
The Southern Oscillation Index tracks differences in air pressure between the eastern and western sides of the tropical Pacific.
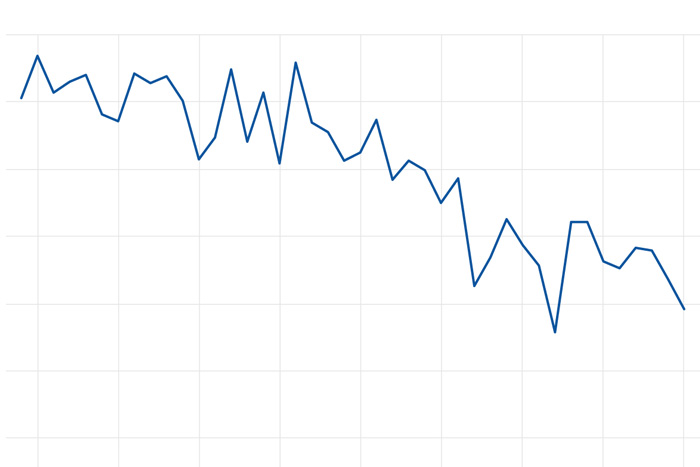
The amount of sea ice that survives the Arctic summer has declined by 13 percent per decade since the start of the 43-year satellite record.
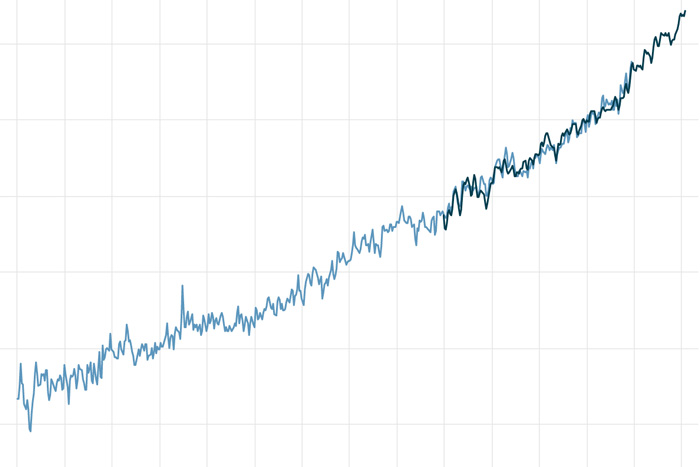
Global average sea level has risen 8-9 inches since 1880, and the rate is accelerating thanks to glacier and ice sheet melt.
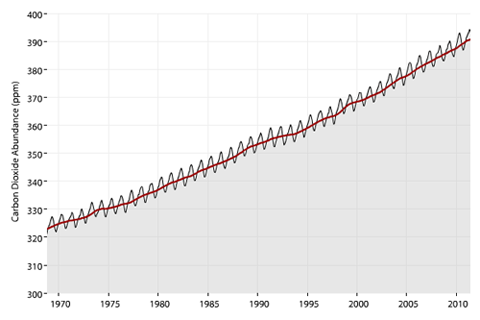
In the past 60 years, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased 100 times faster than it did during the end of the last ice age.
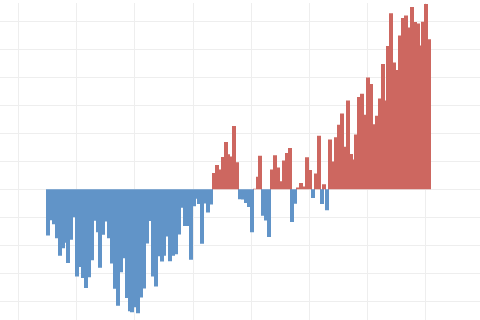
Earth's surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the start of the NOAA record in 1850. It may seem like a small change, but it's a tremendous increase in stored heat.
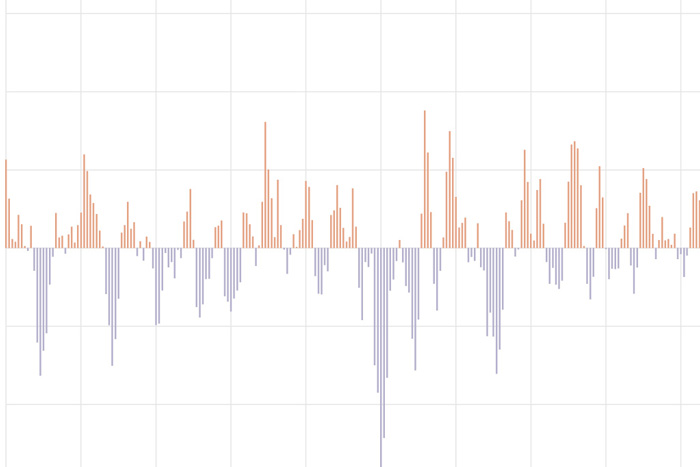
The Arctic Oscillation (AO) refers to an atmospheric circulation pattern over the mid-to-high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. The most obvious reflection of the phase of this oscillation is the north-to-south location of the storm-steering, mid-latitude jet stream.
