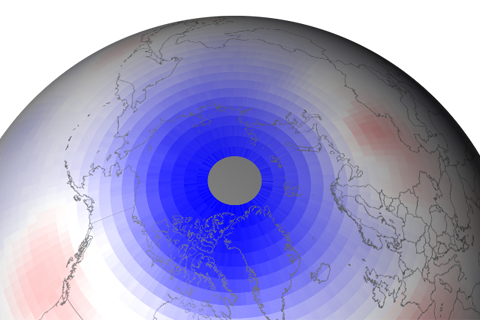
Compared to the large ozone hole that forms over Antarctica each year, Arctic ozone loss has generally been much more limited. But in 2011, Arctic ozone declined to surprisingly low levels. What did climate have to do with it?

Compared to the large ozone hole that forms over Antarctica each year, Arctic ozone loss has generally been much more limited. But in 2011, Arctic ozone declined to surprisingly low levels. What did climate have to do with it?

The remnants of Tropical Storm Lee brought record rainfall amounts to the East Coast in the first week of September, swelling rivers and forcing evacuations in some areas of Pennsylvania and New York.

An intense drought has gripped the southern tier of the United States for several months, accompanied by destructive wildfires, low water supplies, and failed crops.

The Brazos River runs dry in Knox County, Texas, in summer 2011.

Ponds that were built to hold significant amounts of water for cattle are dwindling away under the hot temperatures, dry winds and lack of rain.
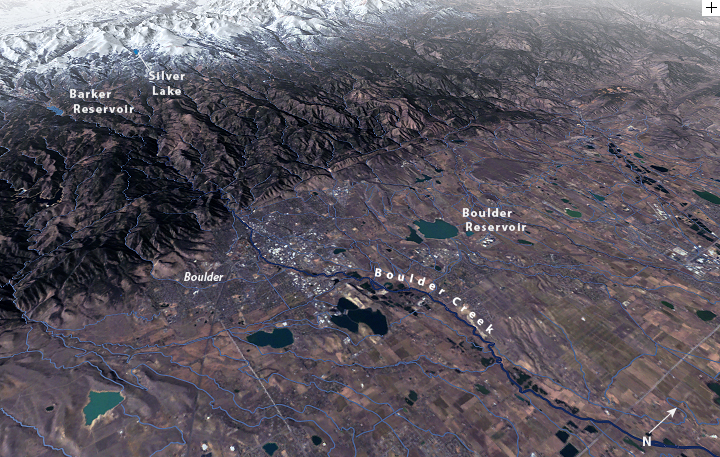
For decades, the City of Boulder, Colorado, has been successfully managing its water supply despite the challenges of being located in a semi-arid climate. But a local water manager wonders if climate change will change the rules of the game...
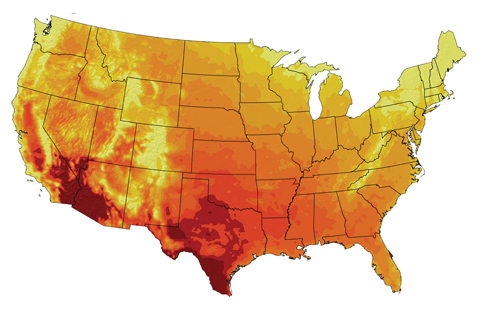
Climate models project that 100-degree days will become more numerous and widespread by the end of the century if greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise.
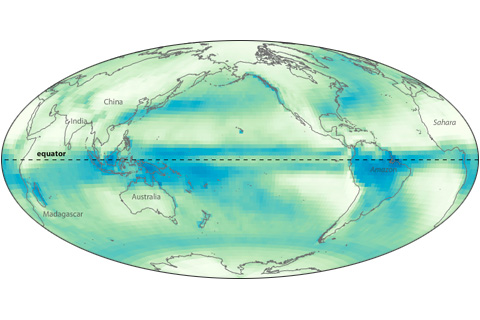
Near the Earth’s equator, solar heating is intense year round. Converging trade winds and abundant water vapor all combine to produce a persistent belt of daily showers known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
As far back as August 2010, NOAA's seasonal climate models predicted that rainfall would be heavier than normal across Indonesia and Southeast Asia in early 2011. The cause? La Niña.
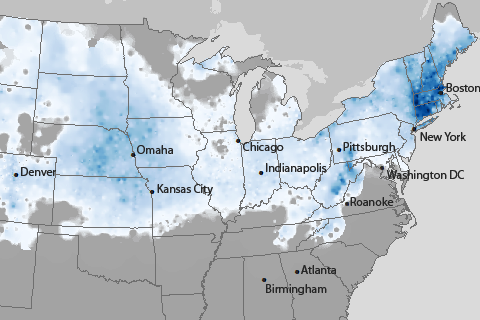
How did this year’s storms compare to the worst in recent history?