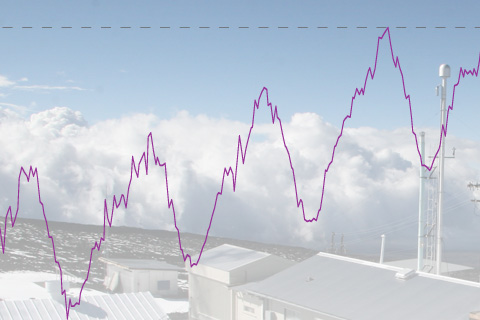
The annual average concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere stood at 395.3 parts per million (ppm) in 2013—a 27 percent increase compared to conditions before the Industrial Revolution. On May 9, 2013, the daily average concentration of CO2 surpassed 400 ppm for the first time at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii.

Since 2004, researchers in NOAA’s Global Monitoring Division have released the Annual Greenhouse Gas Index: a single value that compares the total warming effect of each year's concentrations of heat-trapping gases to 1990 levels.

In response to recent decades' warming, forests in the eastern United States have been "inhaling" more carbon dioxide through photosynthesis than they've “exhaled” through respiration.
CarbonTracker is a tool for modelling sources and sinks of carbon dioxide. Users can download the code, carbon dioxide data, and the tool's carbon flux estimates to conduct their own analyses or to help improve the system.

Ocean water acidified by increasing carbon dioxide is corroding calcium carbonate minerals—an essential ingredient for shell- and skeleton-building that creatures like this tiny snail rely upon.

Like a prehistoric fly trapped in amber during dinosaurs' days, airborne relics of Earth's earlier climate can end up trapped in glacial ice for eons. How do climate scientists turn those tiny relics into a story about Earth's ancient climate?
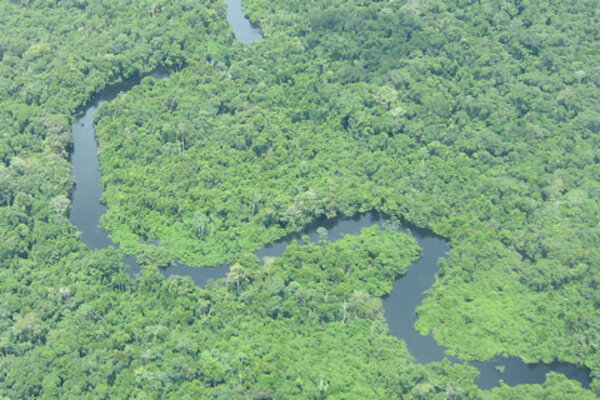

How drought affects carbon balance in the Amazon
March 6, 2014
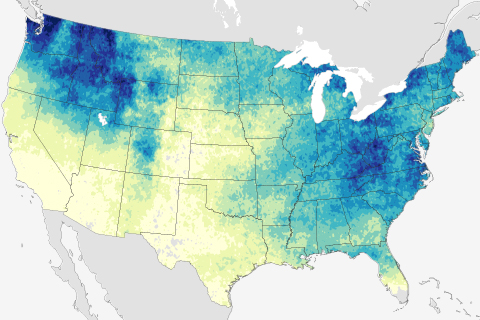
According to the 2009 National Climate Assessment, heavy downpours have increased in frequency and intensity during the last 50 years. Models predict that downpours will become still more more frequent and intense as greenhouse gas emissions and the planet’s temperature continue to rise.
NOAA is expanding ocean measurements of carbon dioxide to under-observed, climate-critical regions by installing a new generation of sensors on the NOAA Ship Ronald H. Brown and several other U.S. government and academic research vessels.
Released in 2023, the Fifth National Climate Assessment (NCA5) includes an Art × Climate gallery. This work by Tami Phelps focuses on the changing ecosystem in Alaska.