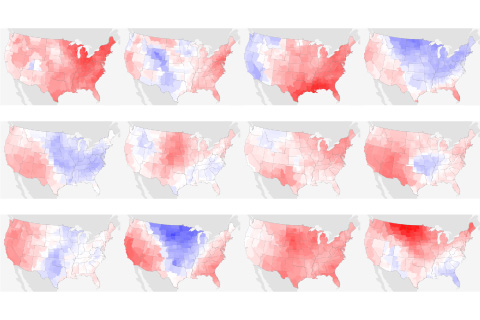
Nationwide warmth was accompanied by extreme precipitation differences: dry conditions in the West and wet conditions in much of the East.
Por una gran mayoría, los científicos del clima están de acuerdo en que la temperatura global promedio hoy en día es más cálida que en la época preindustrial, y que la actividad humana es el principal factor contribuyente.
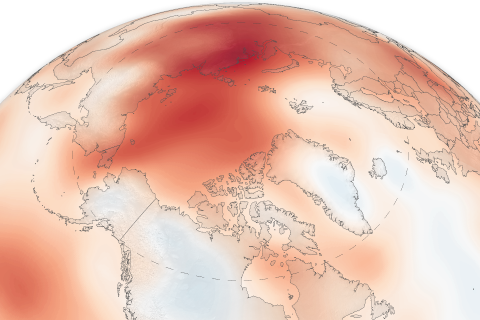
The 15th installment of NOAA's Arctic Report Card NOAA's 15th Arctic Report Card catalogs the numerous ways that climate change continues to disrupt the polar region.

Climate.gov talks with Emily Fischer—an early-career atmospheric scientist and educator who has already made significant contributions to Earth science and fostering greater inclusion of women in the geosciences.
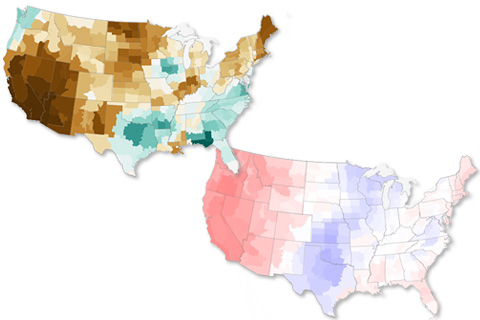
The soaking brought to the Gulf region by tropical cyclones in September 2020 contrasted starkly with the hot, dry conditions in the West.
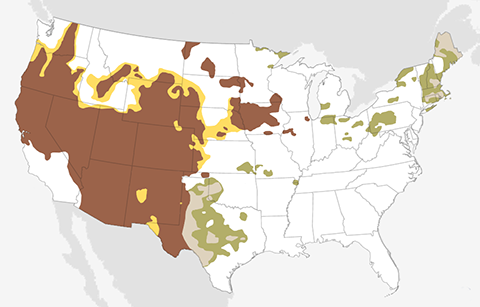
The September 2020 temperature and precipitation outlook favors a warmer- and drier-than-average September across the western United States, and a wetter-than-average month across the south-central Plains and much of the East.
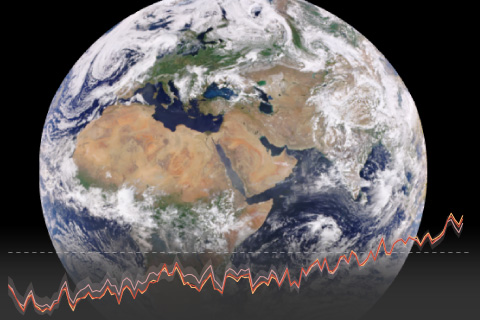
Record-high sea level, noteworthy extreme weather, and rising levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and oceans are just a few of the hundreds of highlights from Earth's annual checkup.

Join three heat experts to talk about how we map, monitor, and lessen the impacts of urban heat islands.
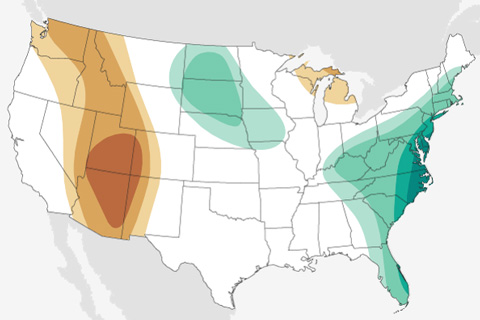
The August 2020 outlook favors hotter-than-average temperatures along both coasts, while tropical moisture is likely to lead to a wetter-than-average August along the East Coast.
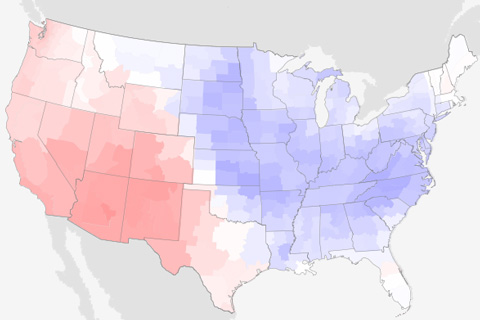
While May 2020 precipitation deficits drew parts of the West deeper into drought, parts of the Upper Midwest, Ohio Valley, and the Southeast got soaked.