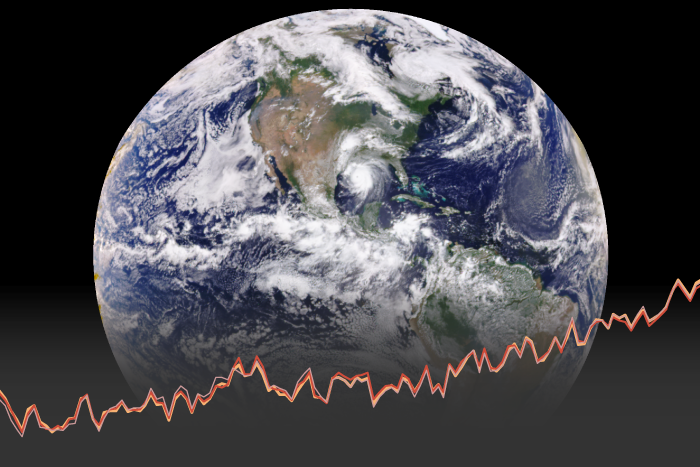
International report confirms 2020 was among three warmest years on record.
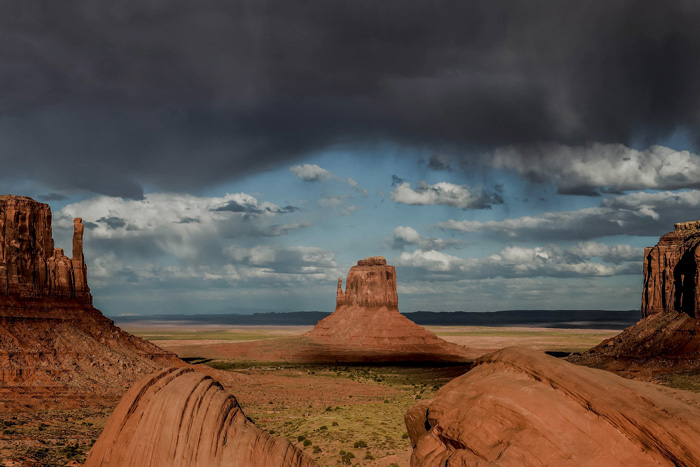

Let's take a tour through North America's summer monsoon, a critical source of rainfall for the U.S. Southwest and Mexico.
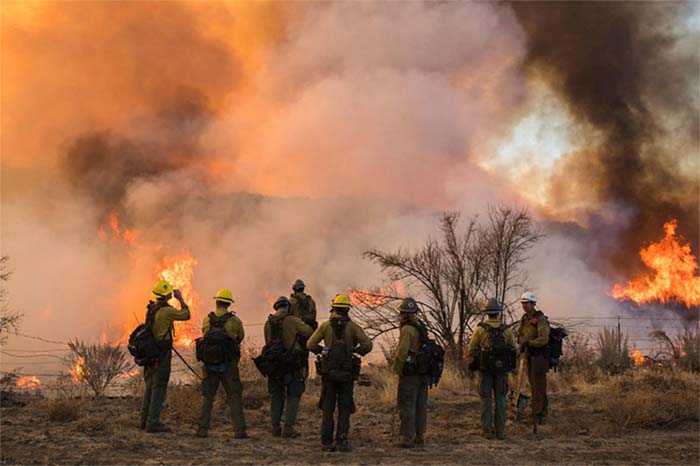

A new study using data from a NOAA-supported field campaign has found that nearly one-fifth of the wildland firefighters in that campaign had smoke exposure above the recommended occupational exposure limit.
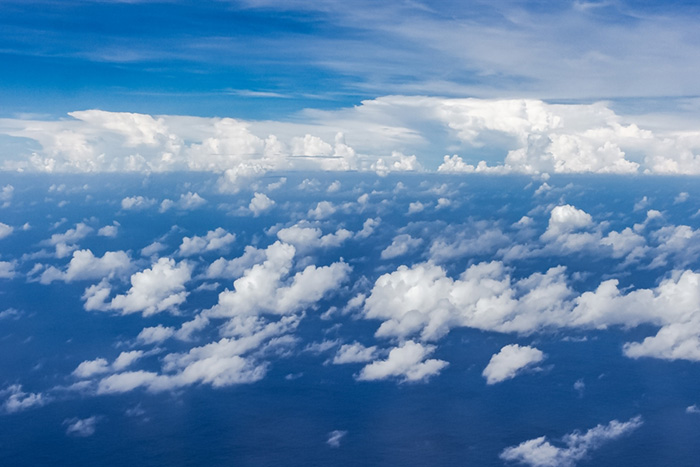

New research on clouds will contribute to a new generation of models aimed at predicting weather and climate.
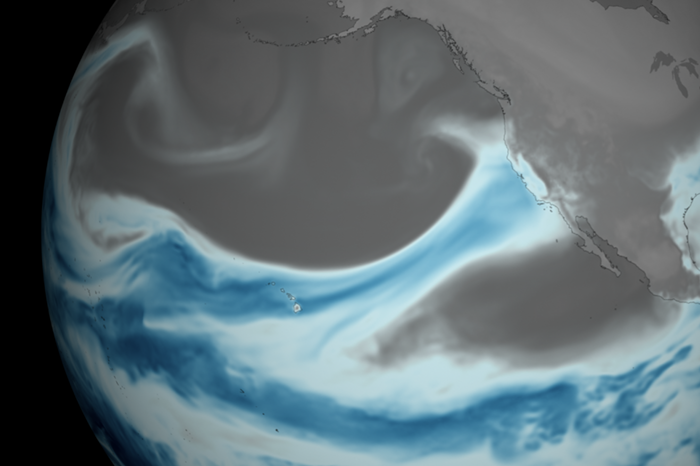
Almost one-third of the mountain snowpack in the Upper Colorado River Basin owes its existence to atmospheric rivers, according to newly published research.
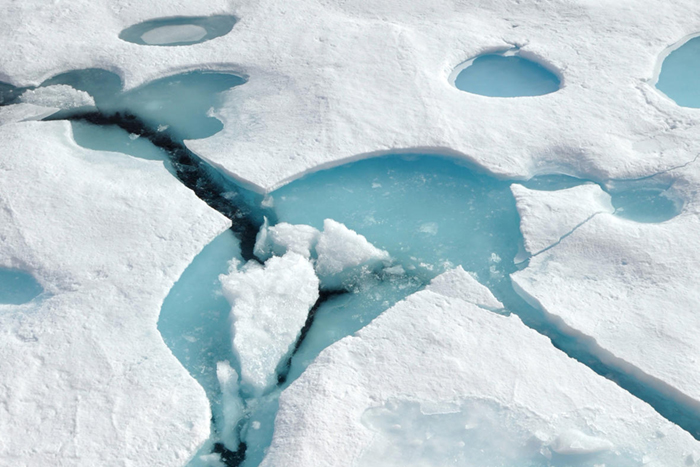

Starting on October 5, 2021, a pair of team members with the Alaska Center for Climate Assessment are set to lead a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) to educate participants about what climate change looks like in the Arctic.
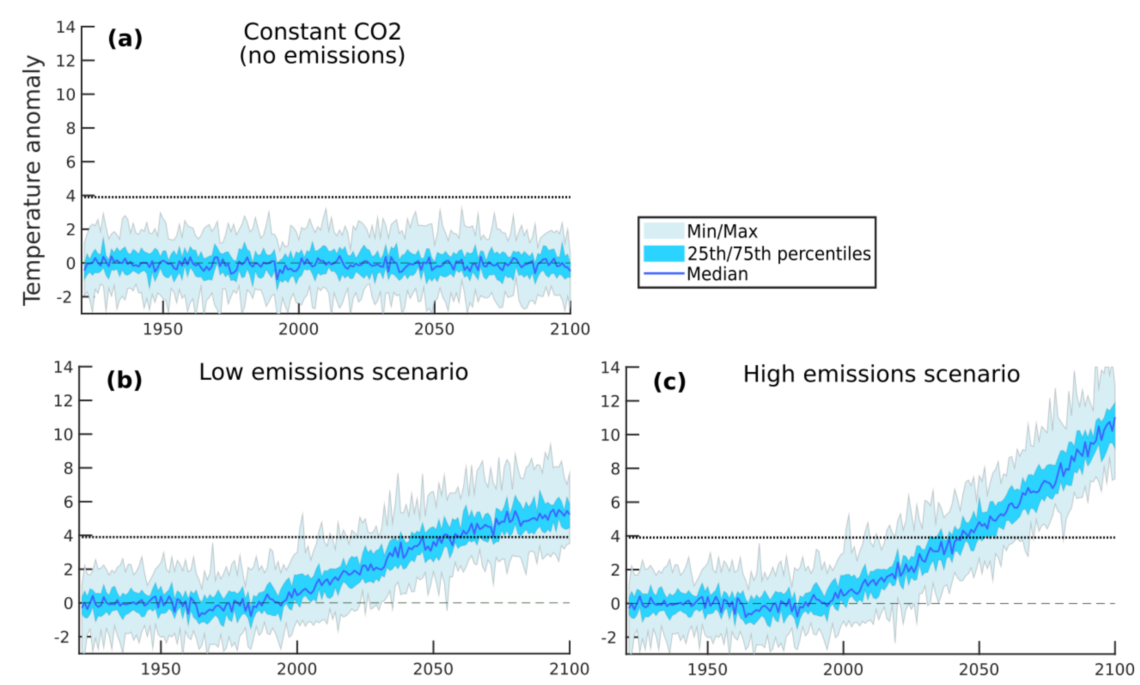
An extreme heat event, breaking all previous records, occurred over southwestern Alaska in the summer of 2019. Analyses using a new high-resolution climate model suggest that the extreme heat event was made up to 6 percent more likely by the impacts of increasing greenhouse gases.
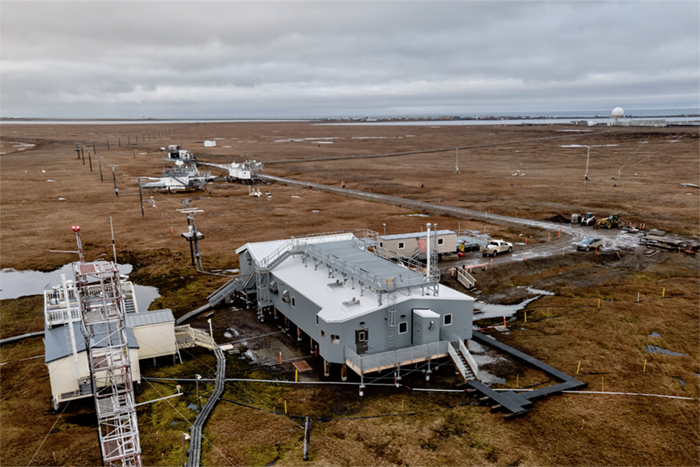

How do plants affect the carbon cycle in the Arctic? Simply measuring carbon dioxide doesn’t answer that question clearly, but new research indicates that measuring carbonyl sulfide gives researchers more clarity on plants’ role.
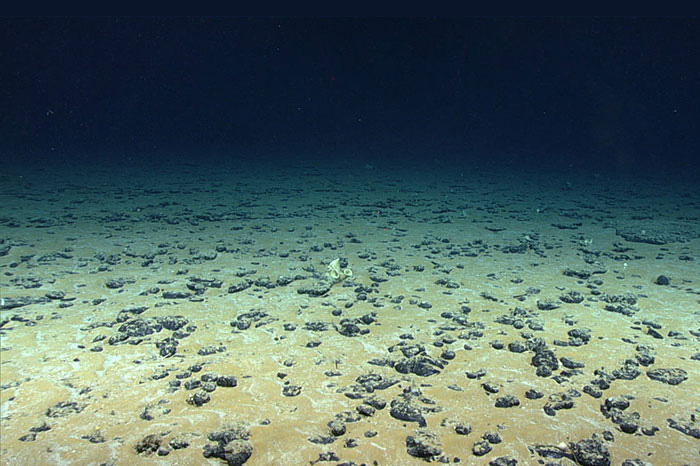

New research describes a potential form of carbon sequestration. The method involves converting decaying vegetation into a form of biocoal called Black Pellets and depositing those pellets in the deep ocean.

The National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) added two new interactive features on Drought.gov that will make it easier for decision makers and the public across the United States to share timely, reliable drought information.