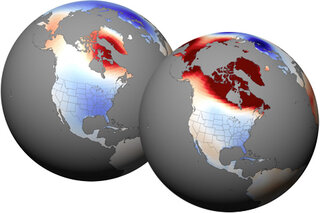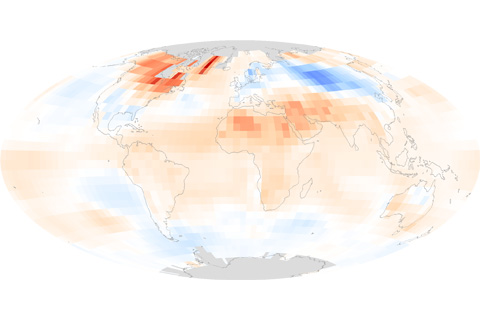
Two natural climate patterns, the Arctic Oscillation and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, had strong influences on the patterns of unusually warm and unusually cool spots worldwide in early and late 2010.
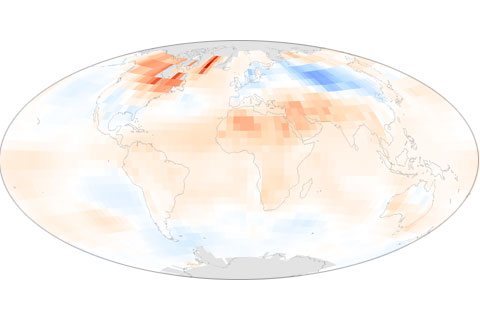
In 2010, global temperatures were marked by near-record warmth and strong natural variability. This is the first in a series of posts highlighting findings from the "State of the Climate in 2010" report.

In the Arctic, an ocean is surrounded by continents, while Antarctica is continent surrounded by oceans. These differences in the arrangement of land and water contribute to differences in each polar region’s climate, oceanic and atmospheric circulation patterns, and seasonal and long-term sea ice patterns.
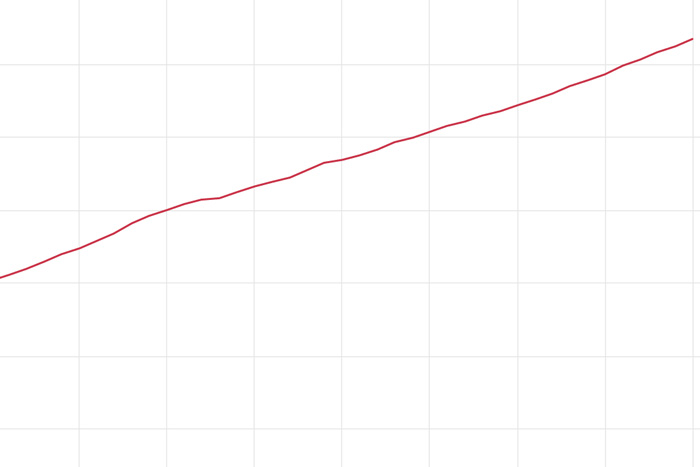
As of 2023, the warming effect of long-lived greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere had increased by 51% compared to 1990. Relative to pre-industrial times, today's atmosphere absorbs more than 3 extra watts of energy per square meter.

Above-average sea surface temperatures, a natural cycle of increased hurricane activity, and a fading La Nina have influenced the 2011 Atlantic hurricane outlook.
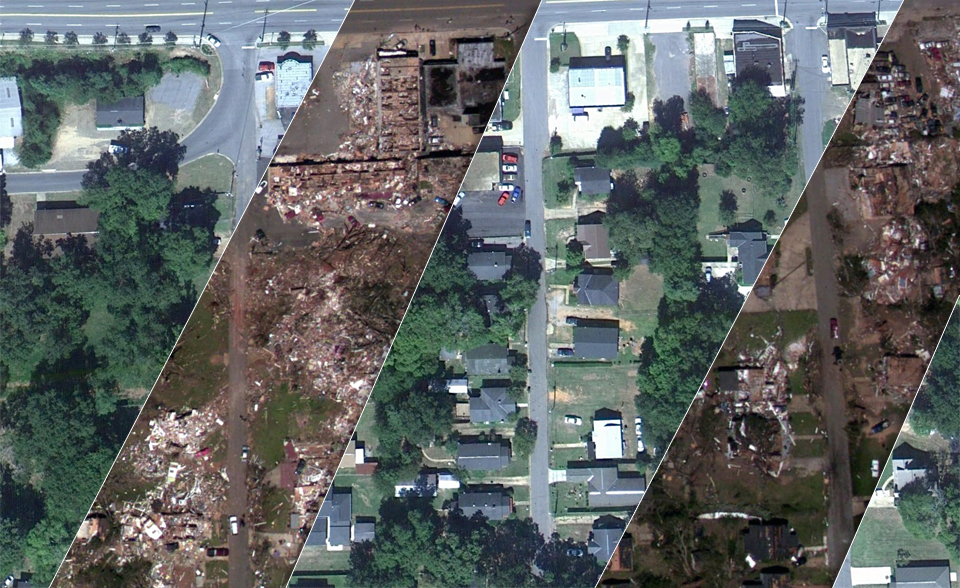

The tornado outbreak across the southern United States in late April 2011 was deadly, devastating, and record breaking. NOAA's "CSI" team is investigating the possible connections between global warming, natural climate patterns, and tornadoes.
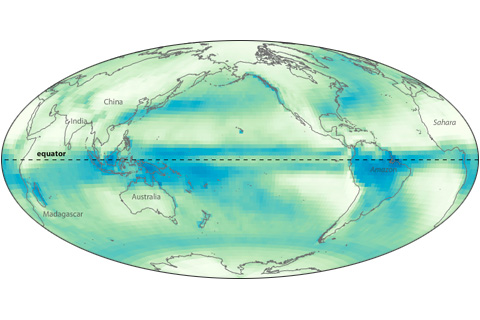
Near the Earth’s equator, solar heating is intense year round. Converging trade winds and abundant water vapor all combine to produce a persistent belt of daily showers known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
As far back as August 2010, NOAA's seasonal climate models predicted that rainfall would be heavier than normal across Indonesia and Southeast Asia in early 2011. The cause? La Niña.
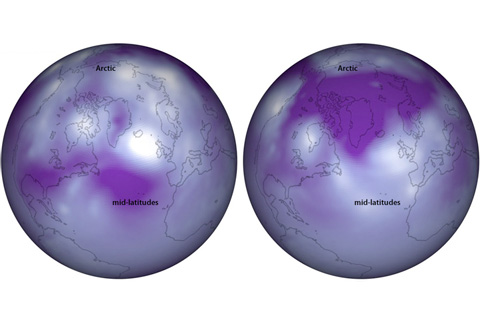
Large-scale shifting of the weight of the atmosphere between mid- and high latitudes creates climate patterns known as the Arctic and North Atlantic Oscillations. These patterns have a big influence on winter weather in the Eastern U.S.