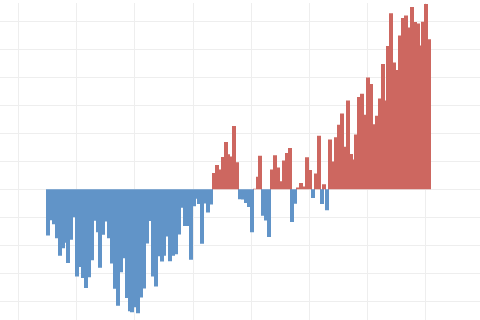
Earth's surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the start of the NOAA record in 1850. It may seem like a small change, but it's a tremendous increase in stored heat.

Earth's surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the start of the NOAA record in 1850. It may seem like a small change, but it's a tremendous increase in stored heat.
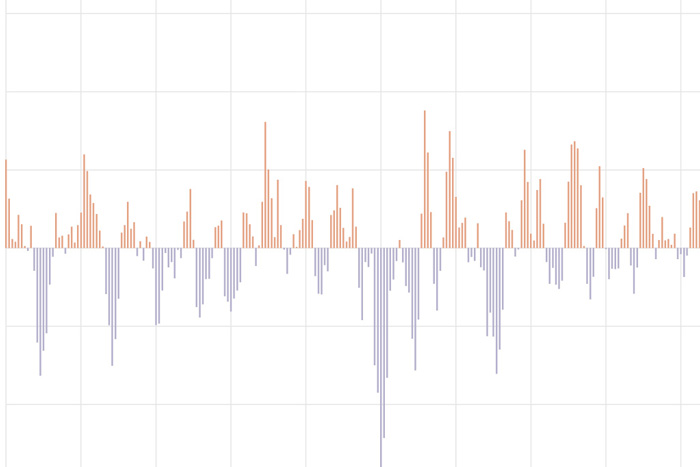
The Arctic Oscillation (AO) refers to an atmospheric circulation pattern over the mid-to-high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. The most obvious reflection of the phase of this oscillation is the north-to-south location of the storm-steering, mid-latitude jet stream.
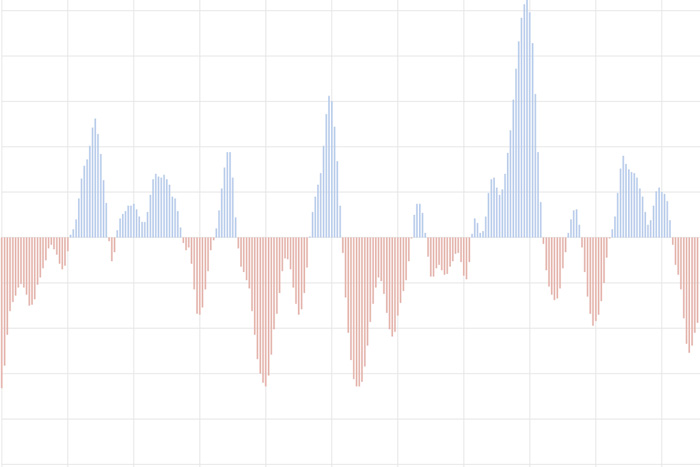
The Oceanic Nino Index tracks the sea surface temperature in the east-central tropical Pacific Ocean. It is NOAA's primary indicator of the climate patterns known as El Niño and La Niña.
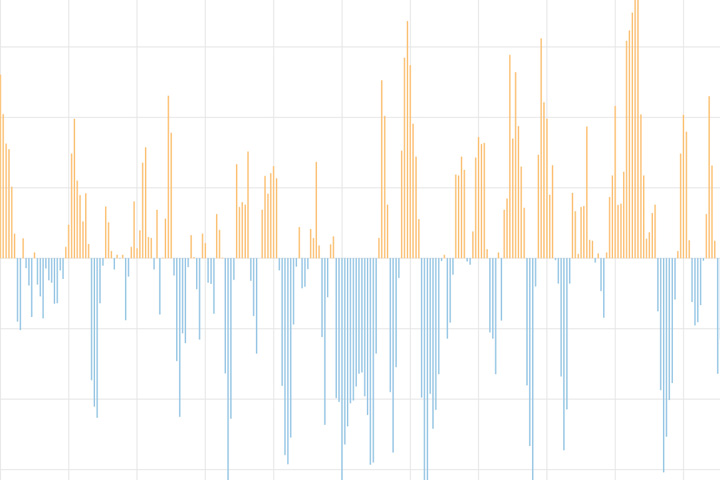
The North Atlantic Oscillation tracks a seesawing of surface pressure between two parts of the North Atlantic. Different phases often bring predictable changes in winds, temperature, and precipitation in the United States and Europe.
Further warming will pose increasing challenges for caribou and the people who depend on them.
Large parts of the North American Arctic had their shortest snow-covered season on record, while parts of Eurasia had a longer-than-average snow-covered season.
Summer sea ice has been stable near these much smaller extents since around 2007.
Heat-driven drying is playing a larger role than low precipitation in 21st-century Western droughts.

November 7, 2024